Capability Template
Capability Template - To determine whether your data are normal, or whether a transformation will be effective for nonnormal data, use individual distribution identification. Using this analysis, you can do the. You can use a capability analysis to determine whether a process is capable of producing output that meets customer requirements, when the process is in statistical control. The results include a capability report for the first method that provides a reasonable fit. Complete the following steps to interpret a normal capability analysis. If you want to perform capability analysis on each of the variables contained in several different columns without having to run a separate analysis for each one, you can use the following. Use a control chart to verify that your process is stable before you perform a capability analysis. If the difference between them is large, there is likely a high amount of variation. There are two basic types of capability measures: Lt means that the process has had ample opportunity to exhibit typical shifts and drifts, cyclical patterns,. If the difference between them is large, there is likely a high amount of variation. Using this analysis, you can do the. Find definitions and interpretation guidance for every potential (within) capability measure that is provided with normal capability analysis for multiple variables. The table of distribution results shows the order of the evaluation of the methods, information about the. To determine whether your data are normal, or whether a transformation will be effective for nonnormal data, use individual distribution identification. Complete the following steps to interpret a normal capability analysis. If you want to perform capability analysis on each of the variables contained in several different columns without having to run a separate analysis for each one, you can use the following. If your data are nonnormal and a. There are two basic types of capability measures: Lt means that the process has had ample opportunity to exhibit typical shifts and drifts, cyclical patterns,. You can assess the effect of variation between subgroups by comparing potential and overall capability. Lt means that the process has had ample opportunity to exhibit typical shifts and drifts, cyclical patterns,. If the difference between them is large, there is likely a high amount of variation. The table of distribution results shows the order of the evaluation of the. Key output includes the histogram, normal curves, and capability indices. To determine whether your data are normal, or whether a transformation will be effective for nonnormal data, use individual distribution identification. The results include a capability report for the first method that provides a reasonable fit. Use normal capability sixpack to assess the assumptions for normal capability analysis and to. To determine whether your data are normal, or whether a transformation will be effective for nonnormal data, use individual distribution identification. Lt means that the process has had ample opportunity to exhibit typical shifts and drifts, cyclical patterns,. If your data are nonnormal and a. Key output includes the histogram, normal curves, and capability indices. The table of distribution results. Use normal capability sixpack to assess the assumptions for normal capability analysis and to evaluate only the major indices of process capability. If the difference between them is large, there is likely a high amount of variation. You can use a capability analysis to determine whether a process is capable of producing output that meets customer requirements, when the process. Use a control chart to verify that your process is stable before you perform a capability analysis. You can use a capability analysis to determine whether a process is capable of producing output that meets customer requirements, when the process is in statistical control. If the difference between them is large, there is likely a high amount of variation. Complete. Key output includes the histogram, normal curves, and capability indices. Use a control chart to verify that your process is stable before you perform a capability analysis. To determine whether your data are normal, or whether a transformation will be effective for nonnormal data, use individual distribution identification. If you want to perform capability analysis on each of the variables. To determine whether your data are normal, or whether a transformation will be effective for nonnormal data, use individual distribution identification. Complete the following steps to interpret a normal capability analysis. The table of distribution results shows the order of the evaluation of the methods, information about the. Use normal capability sixpack to assess the assumptions for normal capability analysis. If the difference between them is large, there is likely a high amount of variation. The results include a capability report for the first method that provides a reasonable fit. To determine whether your data are normal, or whether a transformation will be effective for nonnormal data, use individual distribution identification. Find definitions and interpretation guidance for every potential (within). If you want to perform capability analysis on each of the variables contained in several different columns without having to run a separate analysis for each one, you can use the following. Using this analysis, you can do the. You can use a capability analysis to determine whether a process is capable of producing output that meets customer requirements, when. There are two basic types of capability measures: If the difference between them is large, there is likely a high amount of variation. If your data are nonnormal and a. Find definitions and interpretation guidance for every potential (within) capability measure that is provided with normal capability analysis for multiple variables. Lt means that the process has had ample opportunity. The table of distribution results shows the order of the evaluation of the methods, information about the. Use a control chart to verify that your process is stable before you perform a capability analysis. If the difference between them is large, there is likely a high amount of variation. To determine whether your data are normal, or whether a transformation will be effective for nonnormal data, use individual distribution identification. The results include a capability report for the first method that provides a reasonable fit. Find definitions and interpretation guidance for every potential (within) capability measure that is provided with normal capability analysis for multiple variables. Using this analysis, you can do the. If your data are nonnormal and a. If you want to perform capability analysis on each of the variables contained in several different columns without having to run a separate analysis for each one, you can use the following. Complete the following steps to interpret a normal capability analysis. You can assess the effect of variation between subgroups by comparing potential and overall capability. Use normal capability sixpack to assess the assumptions for normal capability analysis and to evaluate only the major indices of process capability.Difference Between Ability and Capability Definition, Meaning
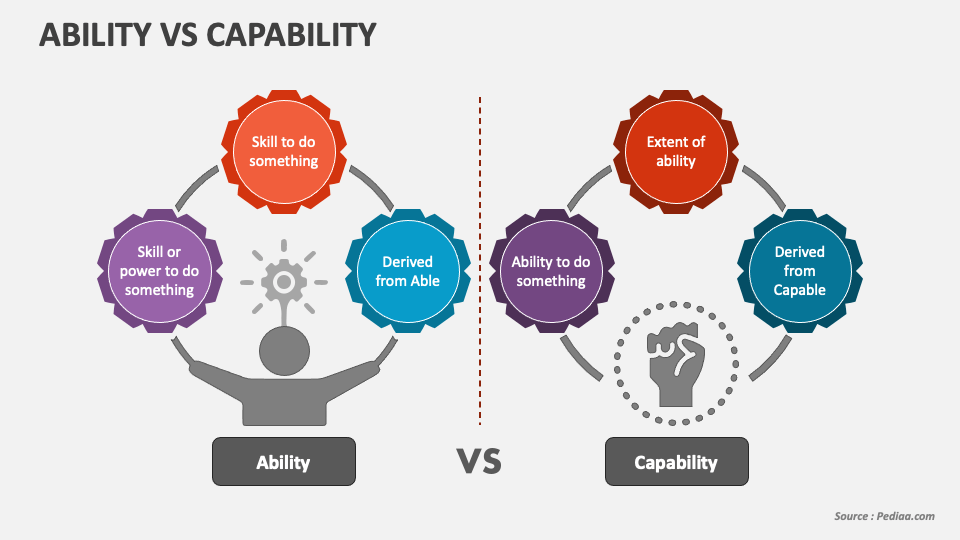
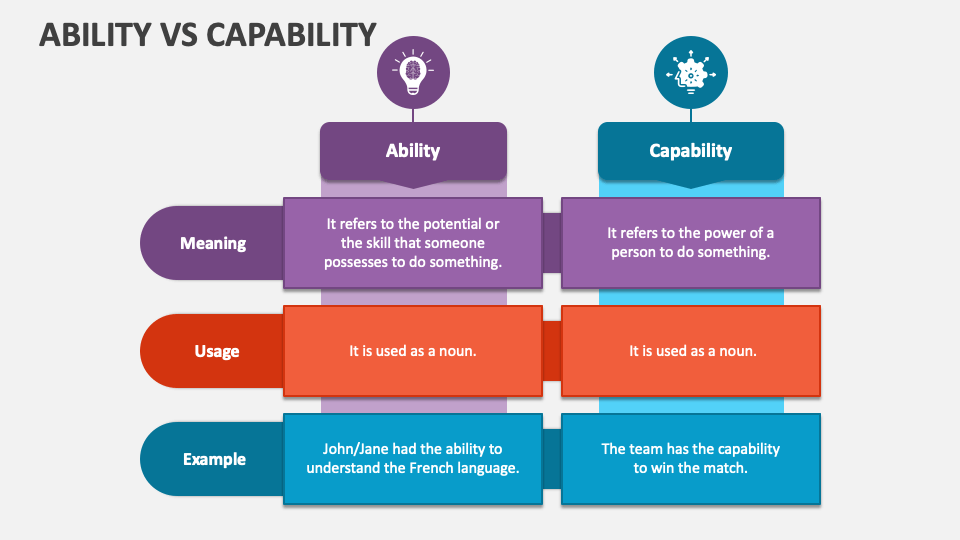
Ability Vs Capability PowerPoint and Google Slides Template PPT Slides
Building Capability Keep your eyes on the Prize! Megan J Buntine
Capability Images Browse 34,989 Stock Photos, Vectors, and Video
Capability Images Browse 35,657 Stock Photos, Vectors, and Video
Free of Charge Creative Commons capability Image Finger 1
Ability Vs Capability PowerPoint and Google Slides Template PPT Slides
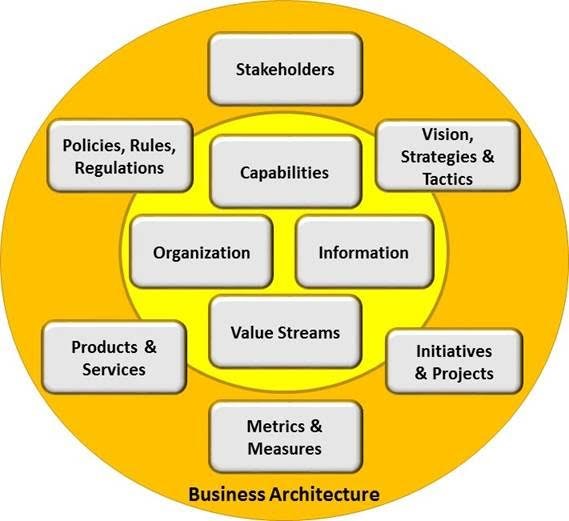
Hypervisors You Must Know Business Capability Model
What is Capabilities? Meaning, Types & Relationship Between Resources
Capability or Competency, which is important to Business? Blue Ocean
There Are Two Basic Types Of Capability Measures:
You Can Use A Capability Analysis To Determine Whether A Process Is Capable Of Producing Output That Meets Customer Requirements, When The Process Is In Statistical Control.
Lt Means That The Process Has Had Ample Opportunity To Exhibit Typical Shifts And Drifts, Cyclical Patterns,.
Key Output Includes The Histogram, Normal Curves, And Capability Indices.
Related Post: